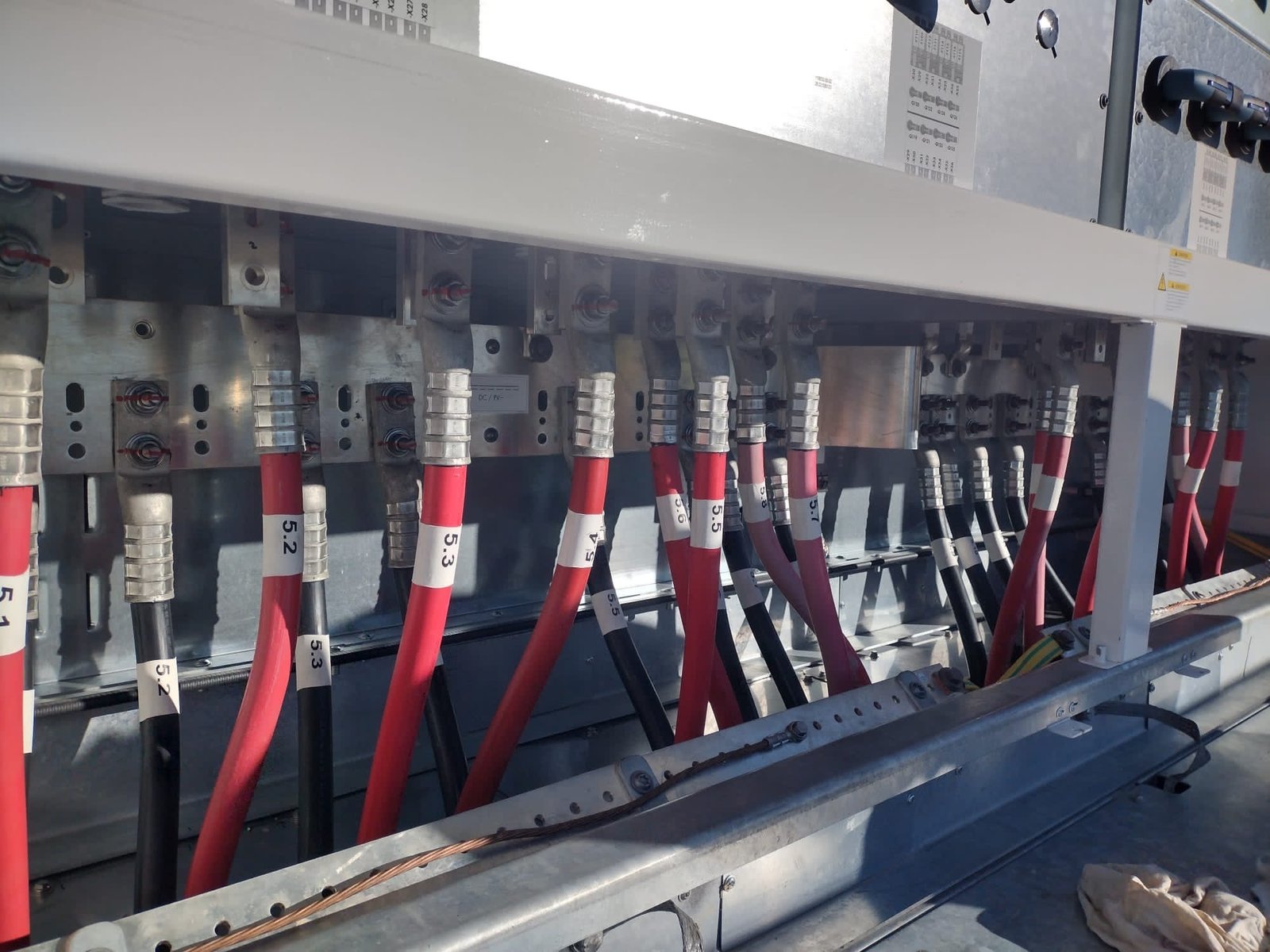
Termination (CBX, Inverters)
Circuit Breaker (CBX) Terminations:
a. Safety Mechanisms:
Circuit Breakers are essential components designed to protect electrical circuits from overloads, short circuits, and other faults. In termination processes, CBX units act as safety mechanisms, automatically interrupting the flow of electricity when abnormal conditions are detected. This prevents potential damage to equipment and ensures the safety of the overall power system.
b. Remote Monitoring and Control:
Modern CBX units come equipped with advanced technologies, enabling remote monitoring and control. This capability allows operators to manage terminations efficiently, perform diagnostics, and even make decisions remotely. Such features enhance the reliability and responsiveness of termination processes, minimizing downtime and improving overall system resilience.
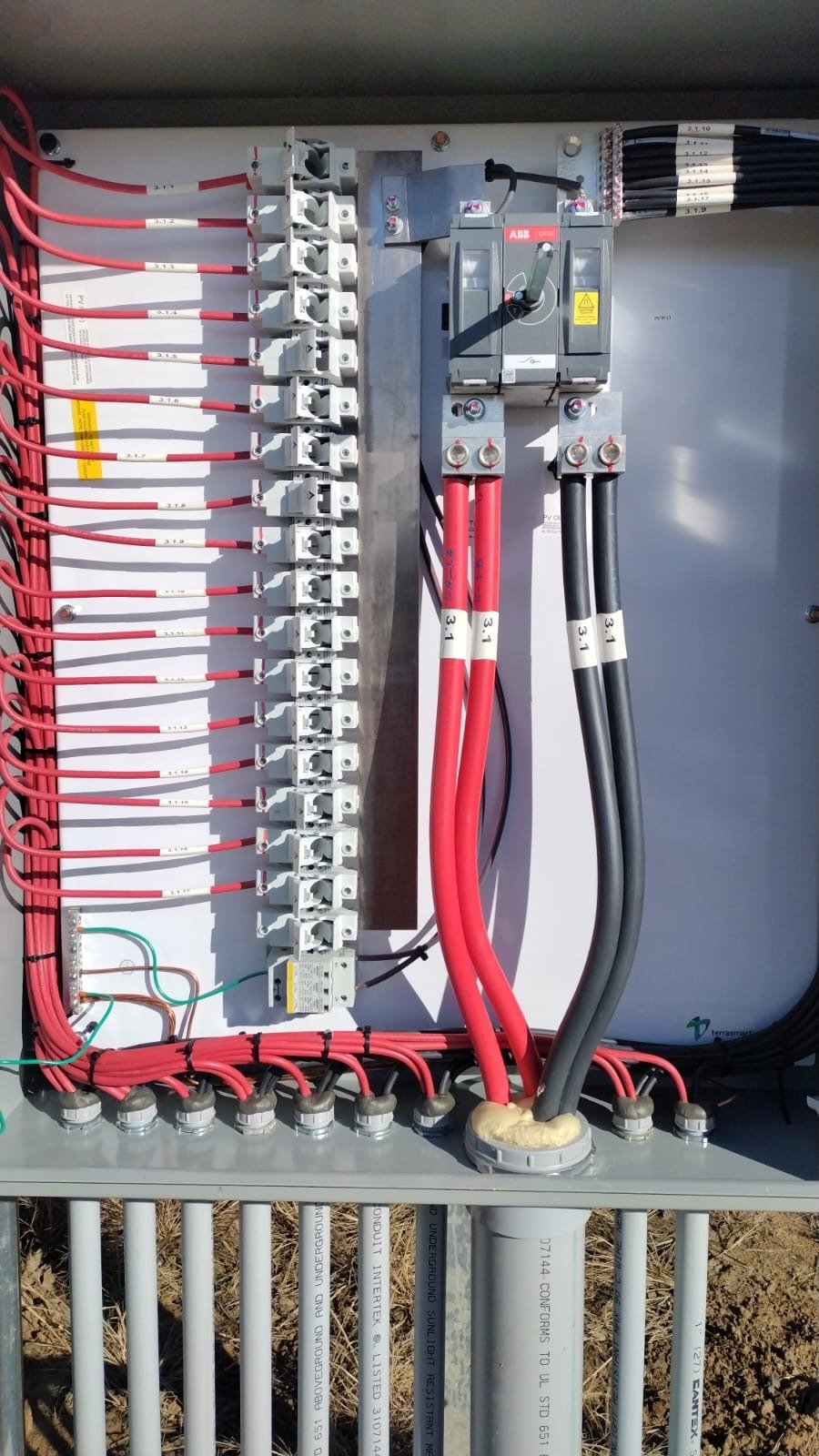
Inverter Terminations:
a. DC to AC Conversion:
Inverters play a crucial role in termination when it comes to systems involving direct current (DC) and alternating current (AC). In renewable energy applications, such as solar or wind power, inverters are responsible for converting the DC generated by solar panels or wind turbines into the AC used in the power grid. This conversion facilitates the seamless integration of renewable energy sources into the existing power infrastructure.
b. Grid Stability and Power Quality:
Inverters contribute to grid stability by regulating the voltage and frequency of the AC power they feed into the grid. This ensures that the power quality meets established standards, preventing disruptions and enhancing the overall stability of the power system. Inverter-based terminations also enable the integration of diverse energy sources, contributing to a more sustainable and resilient energy ecosystem.

